Usuario:Angelito7/Anexo:Músculos del cuerpo humano

Esta es una tabla de los músculos de la anatomía humana.
Hay aproximadamente 640 músculos esqueléticos en el cuerpo humano típico, y casi cada uno de ellos está dispuesto en forma de un par de músculos bilaterales, a ambos lados derecho e izquierdo, dando así lugar a aproximadamente 320 pares de músculos, tal y como se presenta en este artículo. No obstante, el número exacto es dificíl de definir, ya que las diferentes fuentes agrupan los músculos de forma diferente; por ejemplo, considerándolos como partes diferentes de un mismo músculo o como varios músculos separados. Los ejemplos dan una variabilidad de entre 640 y 850.[1]
Los músculos del cuerpo humano pueden categorizarse en grupos que incluyen a los músculos relacionados con la cabeza y el cuello, músculos del torso o tronco, músculos de los miembros superiores, y músculos de los miembros inferiores.
La acción está referida a la acción de cada músculo desde la posición anatómica. En otras posiciones pueden realizarse otras acciones.
Músculos de la cabeza y cuello: la cabeza[editar]
Cuero cabelludo/Párpado[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| occipitofrontalis | 2 vientres occipitales y 2 vientres frontales | galea aponeurótica | nervio facial | eleva las cejas | ||
| corrugator supercilii | arcos superciliares | piel de la frente, próxima a la ceja | nervio facial | arruga la frente | ||
| depressor supercilii | borde orbitario medial | cara medial de la órbita ósea | nervio facial | deprime de la ceja |
_
Músculos extrínsecos del globo ocular[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| levator palpebrae superioris | hueso esfenoides | **tarsal plate, upper párpado | arteria oftálmica | nervio oculomotor | **retracts//elevates párpado | músculo orbicular de los ojos |
| tarsalis superior | underside of músculo elevador del párpado superior | **superior tarsal plate of the eyelid | arteria oftálmica | sistema nervioso simpático | raise the párpado |
Recto:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista superior anillo tendinoso común at the orbital apex 7.5 mm superior to the **corneal limbus nervio oculomotor **elevates, aductos, and **rotates medially the eye inferior anillo tendinoso común at the orbital apex 6.5 mm inferior to the **corneal limbus **inferior branch of oculomotor nerve depression and aducción medial anillo tendinoso común at the orbital apex 5.5 mm medial to the **corneal limbus inferior division of the nervio oculomotor aductos the eyeball lateral anillo tendinoso común at the orbital apex 7 mm temporal to the **corneal limbus nervio abducens abducts the eyeball
Oblícuo:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista superior anillo tendinoso común at the orbital apex, medial to optic canal Outer posterior quadrant of the eyeball lateral muscular branch of the arteria oftálmica nervio troclear primary: **intorsion. secondary:abduct (laterally rotate) and depress the eyeball inferior orbital surface of the maxilar superior, lateral to the **lacrimal groove laterally onto the eyeball, deep to the músculo recto lateral, by a short flat tendon nervio oculomotor **extorsion, elevation, abduction
Intraocular[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| ciliaris | nervio oculomotor (sistema nervioso parasimpáticos) | acomodamiento | ||||
| dilatator pupillae | **superior cervical ganglion (sympathetics) | **pupil dilation | músculo esfínter del iris | |||
| sphincter pupillae | **short ciliary nerves | constricts pupil | músculo dilatador del iris |
Oído[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| auriculares | galea aponeurótica | front of the helix, cranial surface of the pinna | nervio facial | (Wiggle ears) | ||
| temporoparietalis | **Auriculares muscles | galea aponeurótica | ||||
| stapedius | neck of estribo | nervio facial | control the amplitude of sound waves to the oído interno | |||
| tensor tympani | Trompa de Eustaquio | handle of the martillo | arteria timpánica superior | **medial pterygoid nerve from nervio mandibular | tensing the tímpano |
Nariz[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| procerus | From fascia over the lower of the hueso propio de la nariz | skin of the lower part of the frente (anatomía) between the cejas | **Temporal and Lower Zygomatic branch of the facial nerve, (a Buccal branch has also been described) | Draws down the medial angle of the ceja giving expressions of frunción | ||
| nasalis | maxilar superior | Hueso propio de la nariz | **Buccal branch of the facial nerve | Compresses bridge, depresses tip of nose, elevates corners of **nostrils |
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| dilator naris | margin of the nasal notch of the maxilar superior, greater and **lesser alar cartilages | skin near the margin of the **nostril | **Buccal branch of the facial nerve | Dilation of **nostrils |
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| depressor septi nasi | **incisive fossa of the maxilar superior | tabique nasal and back part of the alar part of músculo nasal | **Buccal branch of the facial nerve | Depression of tabique nasal | ||
| levator labii superioris alaeque nasi | maxilar superior | **nostril y labio superior | **buccal branch of the facial nerve | dilates the **nostril; elevates the **upper lip and **wing of the nose |
Boca[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| levator anguli oris | maxilar superior | modiolus of mouth | arteria facial | nervio facial | sonrisa (elevates angle of boca) | |
| depressor anguli oris | tubercle of mandíbula | modiolus of mouth | arteria facial | **mandibular branch of nervio facial | depresses angle of boca |
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| levator labii superioris | **Medial infra-orbital margin | Skin and muscle of the **upper lip (**labii superioris) | arteria facial | **buccal branch of the facial nerve | Elevates the **upper lip | |
| depressor labii inferioris | oblique line of the mandíbula, between the sínfisis and the **mental foramen | integument of the **lower lip, Orbicularis oris fibers, its fellow of the opposite side | nervio facial | depress the **lower lip |
Zygomaticus:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista major anterior of zygomatic modiolus of boca arteria facial **buccal branch of the facial nerve draws angle of boca upward and laterally minor hueso cigomático skin of the **upper lip arteria facial nervio facial, buccal branch elevates **upper lip
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| mentalis | anterior mandíbula | barbilla | **mandibular branch of nervio facial | elevates and wrinkles skin of barbilla, protrudes lower lip | ||
| buccinator | alveolar processes of the **maxillary bone and mandíbula, **pterygomandibular raphe | in the fibres of the músculo orbicular de la boca | arteria bucal | **buccal branch of the facial nerve | compress the cheeks against the teeth (blowing), masticación. | |
| orbicularis oris | Maxilar superior and mandíbula | Skin around the lips | **buccal branch of the facial nerve | pucker the labios | ||
| risorius | glándula parótida fascia | modiolus | arteria facial | **Buccal branch of the facial nerve | draw back angle of boca |
Masticación[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| masseter | arco cigomático y maxilar superior | coronoid process and **ramus of mandible | arteria maseterina | **masseteric nerve (V3) | elevation (as in closing of the mouth) and retraction of mandíbula | Músculo platisma |
| temporalis | **temporal lines on the hueso parietal of the skull | coronoid process of the mandíbula | deep temporal | third branch (nervio mandibular) of the nervio trigémino | elevation and retraction of mandíbula | Músculo platisma |
Pterygoideus:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista lateralis **Great wing of sphenoid and **pterygoid plate Condyle of mandible **pterygoid branches of maxillary artery **external pterygoid nerve from the nervio mandibular depresses mandíbula medialis deep head: medial side of **lateral pterygoid plate behind the upper teeth
superficial head: **pyramidal process of palatine bone and **maxillary tuberositymedial **angle of the mandible **pterygoid branches of maxillary artery nervio mandibular via **nerve to medial pterygoid elevates mandible, closes maxilar, helps lateral pterygoids in moving the jaw from side to side
Lengua[editar]
Extrínsecos[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista | |
| genioglossus | Superior part of mental spine of mandíbula (**symphysis menti) | Dorsum of lengua and body of hioides | Arteria lingual | nervio hipogloso | Complex - Inferior fibers protrude the lengua, middle fibers depress the lengua, and its superior fibers draw the tip back and down | ||
| hyoglossus | hioides | side of the tongue | nervio hipogloso | depresses tongue | |||
| chondroglossus | **lesser cornu and body of the hioides | intrinsic muscular fibers of the lengua | nervio hipogloso | depresses tongue (some consider this muscle to be part of músculo hiogloso) | |||
| styloglossus | Styloid process of temporal bone | tongue | Nervio hipogloso | elevates and retracts tongue | inferior and middle fibers of músculo geniogloso |
Intrínsecos[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| longitudinalis superior | close to the epiglotis, from the **median fibrous septum | edges of the tongue | nervio hipogloso | |||
| transversus | **median fibrous septum | sides of the lengua | nervio hipogloso | |||
| longitudinalis inferior | root of the tongue | apex of the tongue | Nervio hipogloso |
Velo del paladar[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| levator veli palatini | hueso temporal, Trompa de Eustaquio | **palatine aponeurosis | arteria facial | nervio vago | elevates velo del paladar | |
| tensor veli palatini | medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone | **palatine aponeurosis | medial pterygoid of nervio mandibular | tension of the velo del paladar | ||
| uvulae | **hard palate | **palatine aponeurosis | pharyngeal plexus | |||
| palatoglossus | **palatine aponeurosis | lengua (anatomía) | nervio vago and cranial nervio accesorio | raising the back part of the lengua (anatomía) | ||
| palatopharyngeus | **palatine aponeurosis and **hard palate | Upper border of cartílago tiroides (blends with constrictor fibers) | Arteria facial | nervio vago and cranial accessory nerve | pulls faringe y laringe |
Faringe[editar]
Constrictor pharyngis:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista inferior cartílago cricoides y cartílago tiroides **pharyngeal raphe external laryngeal branch of the nervio vago Swallowing medius hioides **pharyngeal raphe Nervio vago Swallowing superior **medial pterygoid plate, **pterygomandibular raphé, alveolar process **pharyngeal raphe, **pharyngeal tubercle Nervio vago Swallowing
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| stylopharyngeus | Apófisis estiloides | cartílago tiroides (pharynx) | nervio glosofaríngeo | elevate the laringe, elevate the pharynx, swallowing | ||
| salpingopharyngeus | cartilage of the Trompa de Eustaquio | posterior fasciculus of the **pharyngopalatinus muscle | nervio vago and cranial accessory nerve | raise the nasofaringe |
Laringe[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| cricothyroideus | Anterior and lateral cricoid cartilage | Inferior cornu and lamina of the cartílago tiroides | external laryngeal branch of the nervio vago | tension and elongation of the cuerdas vocales (has minor adductory effect) |
Cricoarytenoideus:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista posterior posterior part of the cartílago cricoides muscular process of the **arytenoid cartilage recurrent laryngeal branch of the nervio vago abducts and **laterally rotates the cartilage, pulling the **vocal ligaments away from the midline and forward and so opening the **rima glottidis **Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle lateralis lateral part of the arch of the cartílago cricoides muscular process of the **arytenoid cartilage recurrent laryngeal branch of the nervio vago adduct and **medially rotate the cartilage, pulling the **vocal ligaments towards the midline and backwards and so closing off the **rima glottidis
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| arytenoideus | **Arytenoid cartilage on one side | **Arytenoid cartilage on opposite side | recurrent laryngeal branch of the nervio vago | approximate the arytenoid cartilages (close **rima glottidis) | ||
| thyroarytenoideus | Inner surface of the cartílago tiroides (anterior aspect) | Anterior surface of **arytenoid cartilage | recurrent laryngeal branch of the nervio vago | thickens the vocal folds and decreases length; also helps helps to adduct the cuerdas vocales during speech |
Músculos of head and neck: el cuello[editar]
Cervical[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| platysma | inferior clavícula and fascia of chest | mandíbula | **cervical branch of the facial nerve (CN VII) | Draws the corners of the boca terminología anatómica de localización and widens it (as in expressions of sadness and fright). Also draws the piel del cuello superiorly when **teeth are clenched | Masetero, Temporal | |
| sternocleidomastoideus | **manubrium sterni, medial portion of the clavícula | **mastoid process of the temporal bone, **superior nuchal line | arteria occipital and the arteria tiroidea superior | motor: nervio accesorio sensory: plexo cervical |
Acting alone, tilts head to its own side and rotates it so the face is turned towards the opposite side.
Acting together, flexes the neck, raises the sternum and assists in forced inspiration. || |
Suprahyoid[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| digastric | anterior belly - digastric fossa (mandíbula); posterior belly - apófisis mastoides of hueso temporal | Intermediate tendon (hioides) | anterior belly - nervio mandibular of the nervio trigémino (CN V) via the **mylohyoid nerve; posterior belly - nervio facial (CN VII) | Opens the jaw when the masetero and the músculo temporal are relaxed. | ||
| stylohyoid | apófisis estiloides | **greater cornu of hioides | nervio facial (CN VII) | Elevate the hyoid during swallowing | ||
| mylohyoid | **Mylohyoid line (mandíbula) | Median raphé | **mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery | **mylohyoid nerve, from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3] | Raises oral cavity floor, **elevates hioides, depresses mandíbula | |
| geniohyoid | **Symphysis menti | hioides | C1 via nervio hipogloso | carry hyoid bone and the tongue upward during deglutition |
Infrahyoid/Strap[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| sternohyoid | **manubrium of sternum | hioides | **ansa cervicalis | depress hyoid bone | ||
| sternothyroid | **manubrium | cartílago tiroides | **Ansa cervicalis | Elevates larynx, may slightly depress hyoid bone | ||
| thyrohyoid | cartílago tiroides | hioides | first cervical nerve | depress hyoid bone | ||
| omohyoid | **Upper border of the scapula | Hioides | **Ansa cervicalis | Depresses the larynx and hyoid bone. Carries hyoid bone backward and to the side |
Vertebral[editar]
Anterior[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| longus colli | Transverse processes of C-3 - C-6 | Inferior surface of the hueso occipital | C2, C3, C4, C5, C6 | Flexes the neck and head | ||
| longus capitis | anterior tubercles of the apófisis transversas of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth vértebra cervical | basilar part of the hueso occipital | C1, C2, C3/C4 | flexión (anatomía) of cuello at **atlanto-occipital joint | ||
| rectus capitis anterior | atlas | hueso occipital | C1 | flexión (anatomía) of cuello at **atlanto-occipital joint | ||
| rectus capitis lateralis | upper surface of the apófisis transversas of the atlas | under surface of the **jugular process of the hueso occipital | C1 | Sidebend at **atlanto-occipital joint |
Lateral[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| scalene | vértebra cervical (C2-C7) | first and second costilla | Arteria cervical ascendente (branch of Arteria tiroidea inferior) | **cervical nerves (C3, C4, C5, C6, C7 | elevation of ribs I&II |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista anterior C3-C6 **first rib Arteria cervical ascendente (branch of Arteria tiroidea inferior) **ventral ramus of C5, C6 medius C2-C6 **first rib Arteria cervical ascendente (branch of Arteria tiroidea inferior) Ventral rami of the third to eighth cervical spinal nerves Elevate 1st rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side posterior transverse processes of C4 - C6 2nd rib Arteria cervical ascendente, arteria transversa del cuello C6, C7, C8 Elevate 2nd rib, tilt the neck to the same side
Músculos del tronco[editar]
Espalda[editar]
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Action Antagonista capitis Ligamentum nuchae, spinous process of C7-T6 Mastoid process of temporal and occipital bone C3, C4 Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head cervicis apófisis espinosa of T3-T6 apófisis transversas of C1, C2, C3 C5, C6
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| músculo erector de la columna | on the spines of the last four vértebra torácica | both the spines of the most cranial vértebra torácica and the vértebra cervical | arterias sacras laterales | **posterior branch of spinal nerve | extends the columna vertebral | Músculo recto mayor del abdomen |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista iliocostalis Sacrum/Illiac Crest/Spinous Processes of lower lumbar/thoracic vertebrae Ribs **Lateral Sacral Artery **longissimus apófisis transversas apófisis transversas arterias sacras laterales **posterior branch of spinal nerve Músculo recto mayor del abdomen músculo espinoso apófisis espinosa apófisis espinosa arterias sacras laterales **posterior branch of spinal nerve Músculo recto mayor del abdomen
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| latissimus dorsi | spinous processes of thoracic T6-T12, **thoracolumbar fascia, cresta ilíaca and inferior 3 or 4 ribs | floor of **intertubercular groove of the húmero | arteria subescapular, arteria dorsal de la escápula | **thoracodorsal nerve | pulls the **forelimb dorsally and terminología anatómica de localización | deltoid, trapezius |
| transversospinales | apófisis transversas | apófisis espinosa | posterior branches |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista **semispinalis dorsi transverse processes of the sixth to the tenth vértebra torácica spinous processes of the upper four thoracic and lower two vértebra cervical **semispinalis cervicis transverse processes of the upper five or six vértebra torácica cervical spinous processes, from the axis to the fifth **Semispinalis capitis Transversal process of lower cervical and higher thoracal columna Area between superior and inferior nuchal line **Greater occipital nerve Extend the head multifidus Hueso sacro, Músculo erector de la columna Aponeurosis, PSIS, and Cresta ilíaca apófisis espinosa Posterior branches Stabilizes vertebrae in local movements of vertebral column rotatores apófisis transversas apófisis espinosa posterior branch
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| interspinales | Apófisis espinosa | Apófisis espinosa | **Posterior rami of nervio espinal | Extensión, flexión (anatomía) and movimiento de rotación of vertebral column. | ||
| intertransversarii | Apófisis transversas | Transverse process above | Anterior rami of nervio espinal | Lateral flexión (anatomía) of trunk |
Suboccipital[editar]
Rectus capitis posterior:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista major Apófisis espinosa of the axis (C2) **Inferior nucheal line of the hueso occipital Dorsal ramus of C1 (**suboccipital nerve) minor the tubercle on the posterior arch of the atlas the medial part of the **inferior nuchal line of the hueso occipital and the surface between it and the foramen magno a branch of the dorsal primary division of the **suboccipital nerve extends the head at the neck, but is now considered to be more of a sensory organ than a muscle
obliquus capitis:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista inferior spinous process of the axis **lateral mass of atlas **suboccipital nerve superior **lateral mass of atlas lateral half of the **inferior nuchal line **suboccipital nerve
**Chest[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| intercostales | ribs 1-11 | ribs 2-12 | arterias intercostales | **intercostal nerves |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista external arterias intercostales **intercostal nerves Inhalación internal internal costilla - inferior border costilla - superior border arterias intercostales **intercostal nerves hold ribs steady external innermost arterias intercostales **intercostal nerves
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| subcostales | inner surface of one costilla | inner surface of the second or third rib above, near its angle | **intercostal nerves | |||
| transversus thoracis | **costal cartilages of last 3-4 ribs, body of sternum, xiphoid process | costilla/**costal cartilages 2-6 | arterias intercostales | **intercostal nerves | depresses ribs | |
| levatores costarum | Apófisis transversas of C7 to T12 vertebrae | Superior surfaces of the ribs immediately inferior to the preceding vertebrae | dorsal rami - C8, T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11 | Assists in elevation of the thoracic rib cage |
serratus posterior:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista inferior vertebrae T11 - L3 the inferior borders of the 9th through 12th costillas arterias intercostales **intercostal nerves depress the lower ribs, aiding in expiration superior **nuchal ligament (or ligamentum nuchae) and the apófisis espinosaes of the columna vertebrale C7 through T3 the upper borders of the 2nd through 5th costillas arterias intercostales 2nd through 5th **intercostal nerves elevate the ribs which aids in inspiration
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| diaphragm | Arteria pericardiofrénica, Arteria musculofrénica, Arteria frénica inferior | phrenic and lower **intercostal nerves | respiration |
Abdomen[editar]
obliques:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista external oblique Lower 8 costae Crista iliaca, **ligamentum inguinale **intercostal nerves T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, **subcostal nerve (T12) Rotates tronco (anatomía) internal oblique **Inguinal ligament, Cresta ilíaca and the **Lumbodorsal fascia Linea alba, Apófisis xifoides and the inferior ribs. **intercostal nerves T8, T9, T10, T11, **subcostal nerve (T12), **iliohypogastric nerve, **ilioinguinal nerve Compresses abdomen and rotates vertebral column.
Pelvis[editar]
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista iliococcygeus **ischial spine and from the posterior part of the **tendinous arch of the pelvic fascia cóccix and **anococcygeal raphe supports the viscera in **pelvic cavity pubococcygeus back of the pubis and from the anterior part of the **obturator fascia cóccix and hueso sacro controls urine flow and contracts during orgasm puborectalis lower part of the sínfisis púbica S3, S4. **levator ani nerve[4] inhibit defecación
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| coccygeus | **Sacrospinous ligament | nervios sacros: S4, S5[3] or S3-S4[5] | closing in the back part of the outlet of the pelvis |
Periné[editar]
sphincter ani:
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista externus S4 and twigs from nervios anales inferiores of nervio pudendo keep the **anal canal and ano closed, aids in the expulsion of the excremento internus nervio pudendo keep the **anal canal and ano closed, aids in the expulsion of the excremento
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista transversus perinei superficialis anterior part of ischial tuberosity central point of perineum nervio pudendo bulbospongiosus Median raphé **Perineal artery nervio pudendo in males, empties the uretra; in females, clenches the vagina ischiocavernosus **Perineal artery nervio pudendo assists the músculo bulbocavernoso
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista transversus perinei profundus inferior rami of the isquion its fellow of the opposite side nervio pudendo sphincter urethrae membranaceae junction of the inferior rami of the pubis and isquion to the extent of 1.25 to 2 cm., and from the neighboring fasciæ its fellow of the opposite side perineal branch of the nervio pudendo (S2, S3, S4) Constricts urethra, maintain urinary continence
Músculos of miembro superiors[editar]
Columna vertebral[editar]
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista rhomboid major apófisis espinosa of the T2 to T5 vertebrae **medial border of the scapula, inferior to the insertion of músculo romboides menor arteria dorsal de la escápula nervio dorsal de la escápula (C4 and C5) Retracts the escápula and rotates it to depress the cavidad glenoidea. It also fixes the scapula to the **thoracic wall. Músculo serrato anterior rhomboid minor **nuchal ligaments and apófisis espinosa of C7- to T1 columna vertebral **medial border of the scapula, superior to the insertion of músculo romboides mayor arteria dorsal de la escápula nervio dorsal de la escápula (C4 and C5) Retracts the escápula and rotates it to depress the cavidad glenoidea. It also fixes the scapula to the **thoracic wall. Músculo serrato anterior
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| levator scapulae | **Posterior tubercles of apófisis transversas of C1 - C4 vertebrae | Superior part of **medial border of scapula | arteria dorsal de la escápula | cervical nerve (C3, C4) and nervio dorsal de la escápula (C5) | Elevates escápula and tilts its cavidad glenoidea inferiorly by rotating scapula |
Thoracic walls[editar]
Hombro[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| deltoid | clavícula, **acromion, **spine of the scapula | **deltoid tuberosity of húmero | primarily arteria circunfleja humeral posterior | Nervio axilar | abducción, flexión y extensión del hombro | Músculo dorsal ancho |
| teres major | posterior aspect of the inferior angle of the escápula | medial lip of the **intertubercular sulcus of the húmero | Subscapular and circumflex scapular arteries | **Lower subscapular nerve (segmental levels C5 and C6) | **Internal rotation of the húmero | |
| Manguito rotador: | Various aspects of scapula | tubérculo mayor del húmero, except subscapularis, which inserts on tubérculo menor del húmero. | lateral rotation (infraspinatus & teres minor), medial rotation (subscapularis), abduction (supraspinatus)[6] |
Brazo[editar]
Anterior compartment[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| coracobrachialis | coracoides process of escápula | medial húmero | arteria braquial | nervio musculocutáneo | flexes & aductos húmero | |
| biceps brachii | short head: **coracoid process of the escápula. long head: **supraglenoid tubercle | **radial tuberosity | arteria braquial | Nervio musculocutáneo (Fascículo lateral: C5, C6, C7) | flexión (anatomía) elbow and supinación antebrazo | Músculo tríceps braquial |
| brachialis | anterior surface of the húmero, particularly the distal half of this bone | coronoid process and the **tuberosity of the ulna | **radial recurrent artery | nervio musculocutáneo | flexión (anatomía) at elbow joint |
Posterior compartment[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| triceps brachii | long head: escápula lateral head: posterior húmero medial head: posterior húmero |
olécranon process of cúbito | Arteria profunda del brazo | nervio radial | extends antebrazo, caput longum aductos hombro | Músculo bíceps braquial |
| anconeus | **Lateral epicondyle of the humerus | lateral surface of the olécranon process and the superior part of the posterior cúbito | Arteria profunda del brazo, **recurrent interosseous artery | nervio radial (C7, C8, and T1) | partly blended in with the músculo tríceps braquial, which it assists in extensión of the antebrazo. Stabilises the elbow and abducts the ulna during pronación. |
Antebrazo[editar]
Anterior compartment[editar]
Superficial[editar]
Deep[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| músculo pronador cuadrado | medial, anterior surface of the ulna | lateral, anterior surface of the radius | arteria interósea anterior | nervio mediano (**anterior interosseous nerve) | pronación the antebrazo | **Supinator muscle |
| flexor digitorum profundus | cúbito | falanges distales | arteria interósea anterior | median (anterior interosseous), muscular branches of ulnar | flex hand, interphalangeal joints | **Extensor digitorum muscle |
| flexor pollicis longus | The middle 2/4 of the volar surface of the radio (geometría) and the adjacent **interosseus membrane. (Also occasionally a small origin slightly on the medial epicondyle of the húmero.) | The base of the distal phalanx of the dedo pulgar | Arteria interósea anterior | **Anterior interosseous nerve (branch of nervio mediano) (C8, T1) | Flexión (anatomía) of the thumb | **Extensor pollicis longus muscle, Músculo extensor corto del pulgar |
Posterior compartment[editar]
Superficial[editar]
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista músculo braquiorradial **Lateral supracondylar ridge of the húmero Distal radio (geometría) (**Radial styloid process) **radial recurrent artery nervio radial Flexión (anatomía) of antebrazo extensor carpi radialis longus **lateral supracondylar ridge 2nd metacarpal arteria radial nervio radial extensión (anatomía) at the muñeca (anatomía), abducts the mano at the muñeca (anatomía) Músculo flexor radial del carpo extensor carpi radialis brevis húmero at the anterior of lateral epicondyle (**common extensor tendon) base of the 3rd metacarpal arteria radial **deep branch of the radial nerve extensión (anatomía) and abductor of the mano at the muñeca (anatomía) Músculo flexor radial del carpo
Deep[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| supinator | **Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, **supinator crest of cúbito, radial collateral ligament, **annular ligament | Lateral proximal **radial shaft | **radial recurrent artery | **posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | supinación antebrazo | Pronator teres, Músculo pronador cuadrado |
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| extensor indicis | cúbito | dedo índice (**extensor hood) | **posterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) | extends dedo índice, muñeca (anatomía) |
Mano[editar]
Lateral volar[editar]
Tenar[editar]
Medial volar[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| palmaris brevis | flexor retinaculum (medial), **palmar aponeurosis | palm | **superficial branch of ulnar nerve | wrinkle skin of palm |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista abductor digiti minimi pisiforme base of the falanges proximales of the 5th digit on the ulnar or medial side arteria ulnar **deep branch of ulnar nerve Abduction of meñique de la mano flexor digiti minimi brevis ganchoso meñique de la mano arteria ulnar **deep branch of ulnar nerve flexión (anatomía) meñique de la mano **Extensor digiti minimi muscle opponens digiti minimi Hook of ganchoso and flexor retinaculum Medial border of 5th metacarpo arteria ulnar **deep branch of ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) Draws 5th metacarpal anteriorly and rotates it, bringing little finger (5th digit) into opposition with thumb
Intermediate[editar]
Muscles of lower limb[editar]
Ilion[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| Iliopsoas | **iliac fossa (iliacus, hueso sacro (iliacus), spine (T12, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5) & intervertebral discs (psoas major, psoas minor)[7] | fémur (anatomía humana) - **lesser trochanter (psoas major/minor), shaft below lesser trochanter (iliacus), tendon of psoas major & femur (iliacus)[7] | arteria circunfleja femoral medial, arteria iliolumbar | nervio femoral, **Lumbar nerves L1, L2 | flexión (anatomía) of articulación coxofemoral (psoas major/minor, iliacus), spine rotation (psoas major/minor) | Músculo glúteo mayor, **posterior compartment of thigh |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista psoas major lower spine in the **lesser trochanter of the fémur (anatomía humana) Arteria iliolumbar Plexo lumbar via anterior branches of L1, L2, L3[2] flexión (anatomía) and **rotates laterally muslo Gluteus maximus psoas minor Side of T12+L1 and IV Disc between Pectineal line and **iliopectineal eminence L1 Weak trunk flexión (anatomía) Gluteus maximus iliacus **iliac fossa **lesser trochanter of fémur (anatomía humana) arteria circunfleja femoral medial, Arteria iliolumbar nervio femoral (L2, L3[2]) flexión (anatomía) and **rotates laterally muslo Gluteus maximus
Nalga[editar]
Muslo[editar]
anterior compartment[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| sartorius | superior to the espina ilíaca antero-superior | medial side of the upper tibia in the pes anserinus | arteria femoral | nervio femoral | flexión (anatomía), **lateral rotation and abduction of muslo; flexión (anatomía) and **medial rotation of leg | |
| quadriceps femoris | combined músculo recto femoral and **vastus muscles | Rótula and **Tibial tuberosity via the Tendón rotuliano | arteria femoral | Nervio femoral | Rodilla extension; Articulación coxofemoral flexión (anatomía) (R.Fem. only) | Músculos isquiotibiales |
posterior compartment/músculos isquiotibiales[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| biceps femoris | tuberosidad isquiática, **linea aspera, fémur (anatomía humana) | the **head of the fibula which articulates with the back of the **lateral tibial condyle | arteria glútea inferior, arterias perforantes, arteria poplítea | long head: nervio tibial, short head: common peroneal nerve | flexes rodilla, **laterally rotates knee joint (when knee is flexed), extends articulación coxofemoral (long head only) | Músculo cuádriceps femoral |
| semitendinosus | tuberosidad isquiática | pes anserinus | arteria glútea inferior, arterias perforantes | sciatic (tibial, L5, S1, S2) | flex rodilla, extend articulación coxofemoral | Músculo cuádriceps femoral |
| semimembranosus | Tuberosidad isquiática | Medial surface of tibia | arteria femoral profunda, gluteal artery | nervio ciático | Articulación coxofemoral extension, Rodilla flexión (anatomía) | Músculo cuádriceps femoral |
medial compartment[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| **adductor muscles of the hip | pubis | fémur (anatomía humana), tibia | nervio obturador | aducción of articulación coxofemoral |
Leg[editar]
anterior compartment[editar]
posterior compartment[editar]
Superficial[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| tríceps sural | tendón de Aquiles, calcáneo | arteria tibial posterior | nervio tibial | flexión plantar |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista gastrocnemius fémur (anatomía humana) calcáneo arterias gemelas nervio tibial from the nervio ciático, specifically, nerve roots S1, S2 flexión plantar, flexión (anatomía) of rodilla (minor) Músculo tibial anterior soleus peroné, medial border of tibia (**soleal line) tendo calcaneus arterias gemelas nervio tibial, specifically, nerve roots L5–S2 flexión plantar Músculo tibial anterior
| plantaris | Lateral supracondylar ridge of fémur (anatomía humana) above lateral head of gastrocnemius | Tendón de Aquiles (medial side, deep to músculo gastrocnemio tendon) | arterias gemelas | nervio tibial | Flexión plantar pie and flexes rodilla | Músculo tibial anterior |
Deep[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| popliteus | middle facet of the lateral surface of the **lateral femoral condyle | posterior tibia under the tibial condyles | arteria poplítea | nervio tibial | **Medial rotation and flexión (anatomía) of knee |
Músculo Origen Inserción Arteria Nervio Acción Antagonista flexor hallucis longus peroné, posterior aspect of upper 1/3 base of distal phalanx of hallux Arteria fibular (peroneal branch of the arteria tibial posterior nervio tibial, S1, S2 nerve roots flexes all joints of the Hallux, flexión plantar of the tobillo joint Músculo extensor largo del dedo gordo flexor digitorum longus medial tibia distal falange (hueso) of lateral four digits arteria tibial posterior Nervio tibial Primary action is Flex digits Extensor digitorum longus, Extensor digitorum brevis tibialis posterior tibia, peroné navicular, medial cuneiform arteria tibial posterior nervio tibial inversion of the foot, flexión plantar of the pie at the tobillo Músculo tibial anterior
lateral compartment[editar]
Peroneus muscles (Fibularis muscles):
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista | |
| Peroneo lateral largo | peroné | **first metatarsal, **medial cuneiform | fibular (peroneal) artery | superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve | flexión plantar, eversion | Músculo tibial anterior | |
| Músculo peroneo lateral corto | peroné | **fifth metatarsal | fibular (peroneal) artery | superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve | flexión plantar, eversion |
Pie[editar]
Dorsal[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| extensor digitorum brevis | calcáneo | dedo del pie | deep peroneal nerve | extends digits 2, 3, and 4 | Flexor digitorum longus, Flexor digitorum brevis | |
| extensor hallucis brevis | calcáneo | base of proximal phalanx of hallux | deep peroneal nerve | Extension of hallux | Músculo flexor corto del dedo gordo |
Plantar[editar]
1st layer[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| abductor hallucis | medial process of calcáneo, flexor retinaculum, **plantar aponeurosis | medial side of base of proximal phalanx of first digit | Plantar nerve | abducts hallux | Músculo aductor del dedo gordo | |
| flexor digitorum brevis | medial process of calcáneo, **plantar aponeurosis, intermuscular septa | middle falange (hueso) of digits 2-5 | Plantar nerve | flexes lateral four toes | Extensor digitorum longus, Extensor digitorum brevis | |
| abductor digiti minimi | Plantar aponeurosis | **Fifth toe or Phalanges | arteria plantar lateral | **lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2) | flex and abduct the **fifth toe | Flexor digiti minimi brevis muscle |
2nd layer[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| quadratus plantae | Calcaneus | Tendons of Flexor Digitorum Longus | **lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2) | Assists Flexor Digitorum Longus in flexion of DIP joints | ||
| lumbrical muscle | tendons of músculo flexor largo de los dedos del pie | medial aspect of extensor expansion over lateral four digits | Plantar nerve | flex proximal falange (hueso) and extend middle and distal falange (hueso) of lateral four digits |
3rd layer[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| flexor hallucis brevis | **medial plantar nerve | flex hallux | Músculo extensor largo del dedo gordo | |||
| adductor hallucis | Plantar nerve | adducts hallux | Músculo abductor del dedo gordo | |||
| flexor digiti minimi brevis | **fifth metatarsal bone | phalanx of the **fifth toe | Plantar nerve | flex and adduct the **fifth toe | Abductor digiti minimi muscle |
4th layer[editar]
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Arteria | Nervio | Acción | Antagonista |
| dorsal interossei | Plantar nerve | abduct dedo del pie | Músculos interóseos plantares | |||
| plantar interossei | metatarso | falanges proximales | Plantar nerve | adduct dedo del pie | Músculos interóseos dorsales del pie |
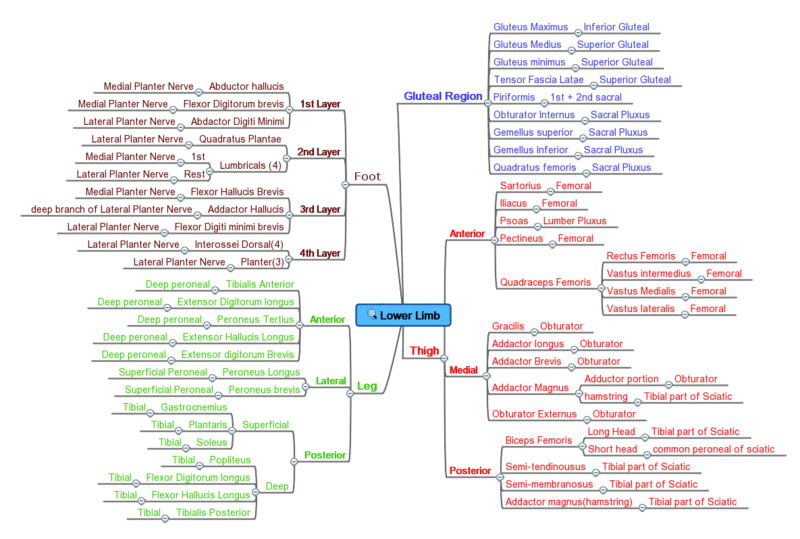
Innervation overview[editar]
Notas[editar]
- ↑ Enotes (en inglés)
- ↑ a b c Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 193
- ↑ a b c Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 217
- ↑ Wallner C, Maas C, Dabhoiwala N, Lamers W, Deruiter M (2006). «Evidence for the innervation of the puborectalis muscle by the levator ani nerve.». Neurogastroenterol Motil 18 (12): 1121-2. PMID 17109696. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2006.00846.x.
- ↑ «uams.edu». Consultado el 9 de diciembre de 2007.
- ↑ List of major muscles of the human body
- ↑ a b exrx.net
Referencias[editar]
- http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/MedEd/GrossAnatomy/dissector/muscles/muscles.html
- http://www.ptcentral.com/muscles/
- http://www.rad.washington.edu/atlas2/
Enlaces externos[editar]
- [1] Tutorial & Quizzes on Skeletal Muscular Anatomy